Growing security needs, new regulations, and the increasing risk of ransomware attacks due to the current geopolitical situation continue to drive European security spending. According to IDC’s Worldwide Security Spending Guide, total European spending will grow 10.6% in 2023. Spending in the region will continue to see almost-double-digit growth over the forecast period, with total spend reaching $71 billion in 2026.
The U.K., Germany, and France are the top spenders on security, together accounting for over half of the European security market. In Central and Eastern Europe, Czech Republic will have the fastest growth in 2023, at over 12% YoY.
„IDC research shows that ongoing disruptions and a dynamic threat landscape have led European organizations to rethink their cyber resilience and proactively ensure their organization maintains good cyber hygiene,“ said Romain Fouchereau, research manager, IDC European Security. „Adopting zero-trust principles to harden security measures and implement secure access controls across networks, applications, and devices has become a top priority, with a defined strategy and support from senior management for new investments and initiatives.“
European spending on software will lead YoY growth in 2023, with approximately 11% YoY growth, but security services will see the largest spending in 2023, reflecting its key role for European organizations across industries.
„We’re seeing that in addition to software and hardware, European companies also have a very real need for security services to guarantee their continued operations and regulatory adherence,“ said Vladimir Zivadinovic, senior research analyst, IDC European Data and Analytics. „This is especially true for organizations with limited competencies in security, especially SMBs in less digitally mature verticals such as media, manufacturing, and healthcare.“
In 2023, the finance sector will have the highest spending in Europe, driven by the need for data protection and regulatory compliance. At the same time, market dynamics are pushing financial institutions to increase their responsiveness and agility. Security services will be pivotal to unlock the full potential of their internal IT teams to focus on new services and improved customer experience.
Finance will be closely followed by manufacturing, with the government sector having the third-largest spending in 2023. Manufacturing will continue to focus on protecting its industrial assets, which will be increasingly connected with the enterprise IT network. The government sector will continue to invest in data protection and in executing its digital transformation initiatives, which are being targeted by ever more sophisticated ransomware attacks.
IDC’s Worldwide Security Spending Guide quantifies the global revenue opportunity for both core and next-generation security purchases with detailed forecast data for security spending by 20 industries across nine regions and 44 countries.
Fachartikel
Studien

Drei Viertel aller DACH-Unternehmen haben jetzt CISOs – nur wird diese Rolle oft noch missverstanden

AI-Security-Report 2024 verdeutlicht: Deutsche Unternehmen sind mit Cybersecurity-Markt überfordert

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
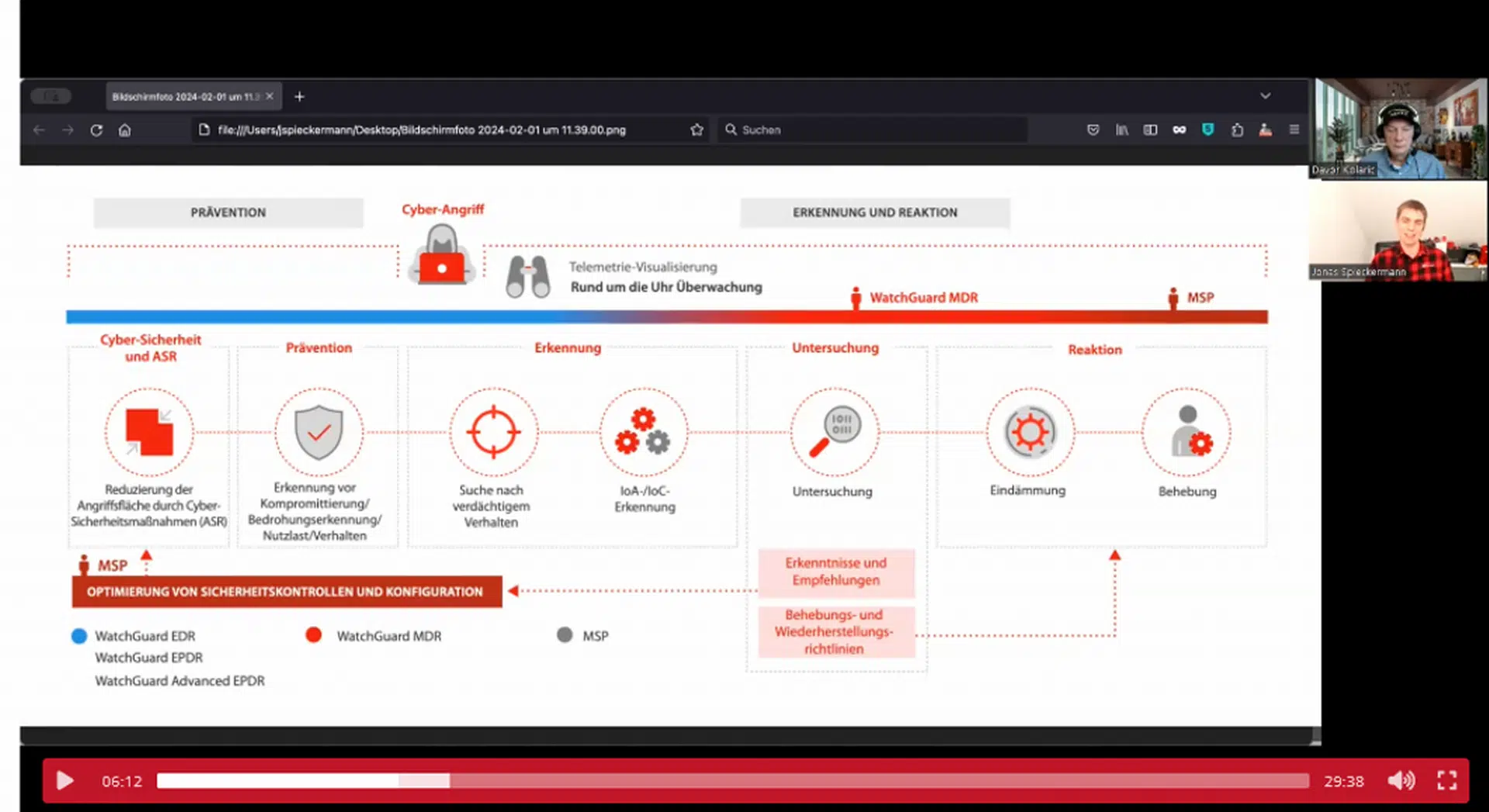
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand