The Council today decided to prolong the framework for restrictive measures against cyber-attacks threatening the EU or its member states for another year, until 18 May 2022.
This framework allows the EU to impose targeted restrictive measures on persons or entities involved in cyber-attacks which cause a significant impact, and constitute an external threat to the EU or its member states. Restrictive measures can also be imposed in response to cyber-attacks against third states or international organisations where such measures are considered necessary to achieve the objectives of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP).
Sanctions currently apply to eight individuals and four entities, and include an asset freeze and a travel ban. Additionally, EU persons and entities are forbidden from making funds available to those listed.
Background
This latest prolongation is part of the EU’s scale up of its resilience and its ability to prevent, discourage, deter and respond to cyber threats and malicious cyber activities in order to safeguard European security and interests.
In June 2017, the EU stepped up its response by establishing a Framework for a Joint EU Diplomatic Response to Malicious Cyber Activities (the „cyber diplomacy toolbox“). The framework allows the EU and its Member States to use all CFSP measures, including restrictive measures if necessary, to prevent, discourage, deter and respond to malicious cyber activities targeting the integrity and security of the EU and its member states.
The EU remains committed to a global, open, stable, peaceful and secure cyberspace and therefore reiterates the need to strengthen international cooperation in order to promote the rules-based order in this area.
- Malicious cyber-attacks: EU sanctions two individuals and one body over 2015 Bundestag hack, press release 22 October 2020
- Council extends cyber sanctions regime until 18 May 2021, press release 14 May 2020
- Council decision concerning restrictive measures against cyber-attacks threatening the Union or its Member States, consolidated text
Fachartikel
Studien

Drei Viertel aller DACH-Unternehmen haben jetzt CISOs – nur wird diese Rolle oft noch missverstanden

AI-Security-Report 2024 verdeutlicht: Deutsche Unternehmen sind mit Cybersecurity-Markt überfordert

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
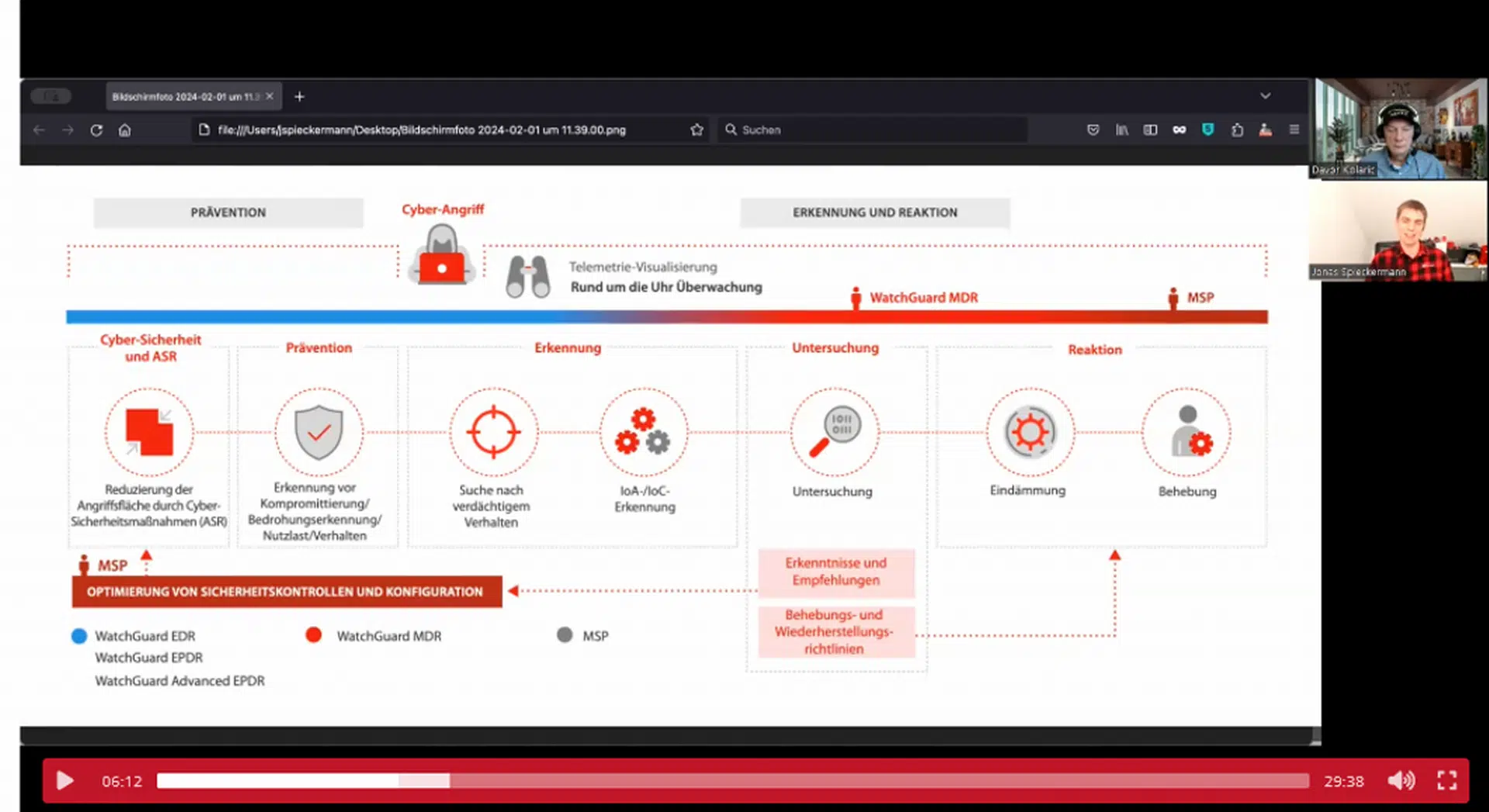
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand