Executive Summary
As the world’s knowledge workers were driven home amid a pandemic and cases of ransomware ran rampant across the internet, measuring the world’s most critical businesses’ internet exposure is more important than ever. In this round of Internet Cyber-Exposure Reports (ICERs), researchers at Rapid7 evaluate five areas of cybersecurity that are both critical to secure to continue doing business on and across the internet, and are squarely in the power of CISOs, their IT security staffs, and their internal business partners to address.
These five facets of internet-facing cyber-exposure and risk include:
1. Authenticated email origination and handling (DMARC)
2. Encryption standards for public web applications (HTTPS and HSTS)
3. Version management for web servers and email servers (focusing on IIS, nginx, Apache, and Exchange)
4. Risky protocols unsuitable for the internet (RDP, SMB, and Telnet)
5. The proliferation of vulnerability disclosure programs (VDPs).
In addition to examining the internet-facing cyber-exposure of the Fortune 500, each section is accompanied by real-world, practical advice that practitioners can start implementing today. Note that this advice is not only for those CISOs who are privileged to hold positions in Fortune 500 companies, but also for those security experts who find themselves in business and regulatory relationships with members of this august collection of corporations.
Through the first half of 2021, Rapid7 will be releasing reports measuring these five critical areas of cybersecurity fundamentals across five of the most advanced economies of the world:
1. The United States Fortune 500 (this report)
2. The United Kingdom’s FTSE 350 (the combined FTSE 100 and FTSE 250)
3. Australia’s ASX 200
4. Germany’s Deutsche Börse Prime Standard 320
5. Japan’s Nikkei 225
Key Takeaways
The paper is divided into five detailed sections covering the areas mentioned above, and the overall takeaways of this research are as follows:
- The Fortune 500 is improving, though slowly and unevenly. At the end of 2020, email security significantly improved among the Fortune 500 as valid Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) configurations grew from 314 to 379 from the end of 2019 (an increase of 13%). Vulnerability disclosure programs (VDPs) similarly gained popularity, especially among the top 100 companies (46% of which have some type of VDP).
- Fundamental cybersecurity exposure issues still trouble the Fortune 500. Unfortunately, outdated and vulnerable versions of popular web and email server applications—as well as nakedly dangerous protocol exposures of Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) and file-sharing (SMB), and Telnet—continue to plague IT administrators across the surveyed companies. We also looked at secure HTTP (HTTPS) and HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) deployment, and found that while HTTPS is in use across the board, HSTS, a key web application security standard that ensures HTTPS is actually used, has only found purchase in the primary domains of about half of the Fortune 500.
- The American healthcare system continues to be especially vulnerable to cyberattack. In a time when healthcare availability is more crucial than ever, the top of the healthcare business sector is especially worrisome. Only about half of healthcare-sector companies have implemented any DMARC controls to properly authenticate email communications. If vulnerabilities are discovered, only 17.5% of the sector appear capable of quickly receiving and acting on those reports. This deficiency in reporting capabilities may be a contributing factor to the outdated versions of Apache and Nginx web servers found running in healthcare IPv4 space, as well as the preponderance of discovered RDP endpoints exposed to the internet.
More here:
https://www.rapid7.com/de/research/reports/2021-industry-cyber-exposure-report/
Autors:
Tod Beardsley, Director of Research at Rapid7
Bob Rudis, Chief Data Scientist at Rapid7
Tom Sellers, Principal Security Researcher at Rapid7
Curt Barnard, Principal Security Researcher at Rapid7
Kwan Lin, Principal Data Scientist at Rapid7
Fachartikel
Studien

Drei Viertel aller DACH-Unternehmen haben jetzt CISOs – nur wird diese Rolle oft noch missverstanden

AI-Security-Report 2024 verdeutlicht: Deutsche Unternehmen sind mit Cybersecurity-Markt überfordert

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
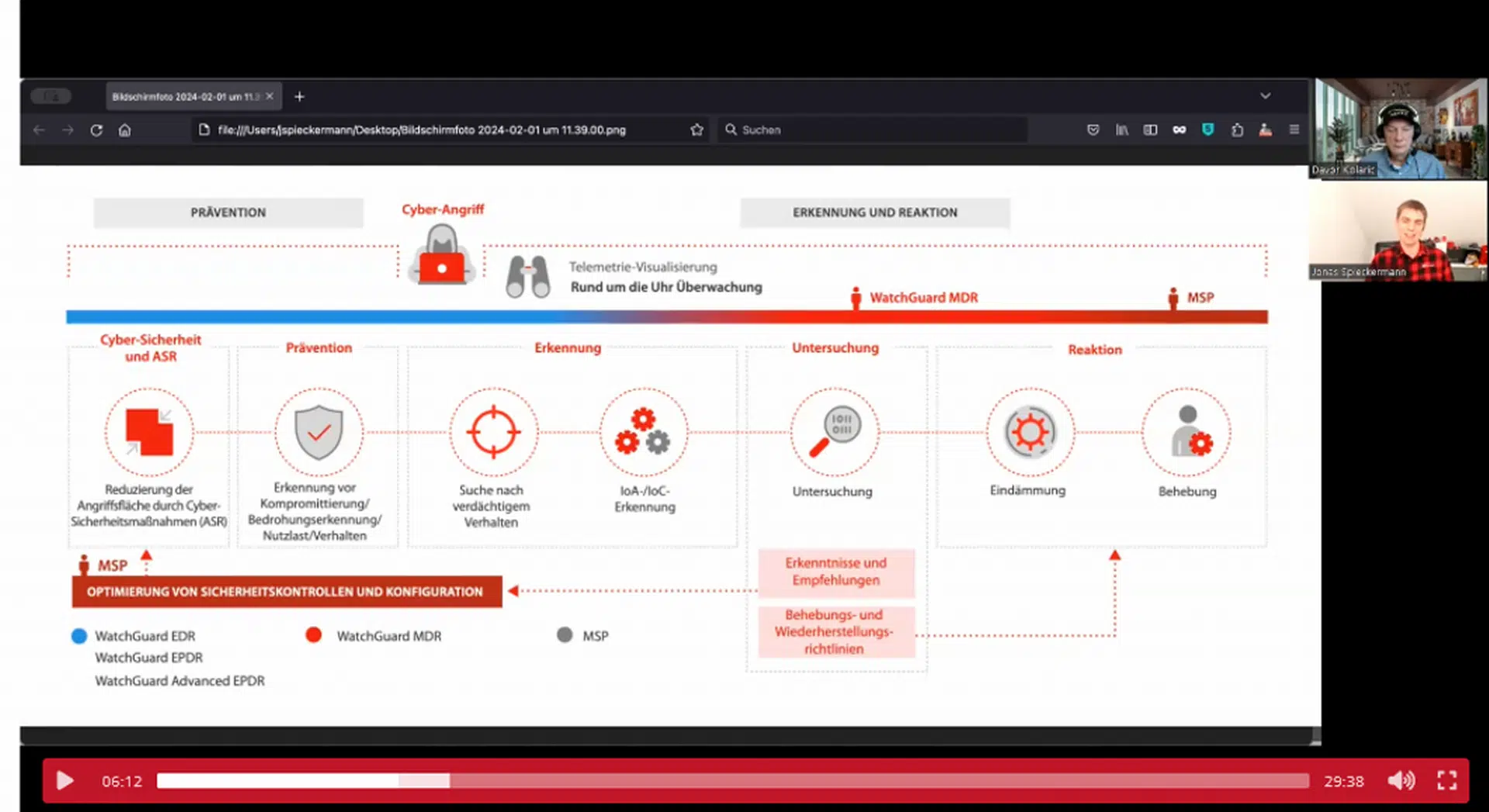
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand