CIOs und CISOs müssen die Verantwortung für die Cybersicherheit mit der Unternehmensleitung teilen
Laut einer neuen Umfrage des Research- und Beratungsunternehmens Gartner betrachten 88 Prozent der Vorstände Cybersicherheit als Geschäftsrisiko und nicht als Technologierisiko. Allerdings verfügen nur 12 Prozent von ihnen über einen speziellen Ausschuss für Cybersicherheit auf Vorstandsebene.
„Es ist an der Zeit, dass Führungskräfte außerhalb der IT Verantwortung für die Sicherheit des Unternehmens übernehmen“, sagt Paul Proctor, Distinguished Research Vice President bei Gartner. „Der Anstieg von Ransomware- und Supply-Chain-Angriffen im Jahr 2021, von denen viele auf betriebliche und unternehmensrelevante Bereiche abzielten, sollte ein Weckruf dafür sein, dass Sicherheit ein Geschäftsthema ist und nicht nur ein weiteres Problem, das die IT-Abteilungen lösen müssen.“
Gartner Survey Finds 88% of Boards of Directors View Cybersecurity as a Business Risk
CIOs and CISOs Must Rebalance Accountability for Cybersecurity So That It Is Shared with Business and Enterprise Leaders
Eighty-eight per cent of Boards of Directors (BoDs) view cybersecurity as a business risk, as opposed to a technology risk, according to a new survey* from Gartner, Inc. However, only 12% of BoDs have a dedicated board-level cybersecurity committee.
“It’s time for executives outside of IT to take responsibility for securing the enterprise,” said Paul Proctor, distinguished research vice president at Gartner. “The influx of ransomware and supply chain attacks seen throughout 2021, many of which targeted operation- and mission-critical environments, should be a wake-up call that security is a business issue, and not just another problem for IT to solve.”
CIOs and CISOs Must Rebalance Cybersecurity Accountability
Even as business leaders are aware of the need to secure the enterprise against new and evolving threats, responsibility for security mostly lies with IT leadership. A recent Gartner survey** found that in 85% of organisations, the CIO, CISO or their equivalent was the top person held accountable for cybersecurity. Just 10% of organisations held non-IT senior managers accountable (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Highest-Level Person in the Organisation Accountable for Cybersecurity
Source: Gartner (November 2021)
“IT and security leaders are often considered the ultimate authorities for protecting the company from threats,” said Proctor. “Yet, business leaders make decisions every day, without consulting the CIO or CISO, that impact the organisation’s security.”
CIOs and CISOs must rebalance accountability for cybersecurity so that it is shared with business and enterprise leaders. Gartner recommends that IT and security leaders work with executives and BoDs to establish governance that shares responsibility for business decisions that affect enterprise security.
Reframe Cybersecurity Investments from a Business Lens
Recent research has found that 66% of CIOs intend to increase cybersecurity investments in the coming year. However, Gartner projections show that overall growth in cybersecurity spend will slow through 2023.
“After years of such heavy investment in security, Boards are now pushing back and asking what their dollars have achieved,” said Proctor.
As security budgets shrink, CIOs and CISOs will need to collaborate closely with executive leadership to reframe cybersecurity investment in a business context. For example, CISOs can offer a range of protection options to business leaders with the costs and risks of each choice clearly outlined.
“CIOs and CISOs must leverage their expertise to increase transparency around investment and risk, to drive shared accountability for security across the business,” said Proctor.
**The 2021 Gartner Global Security and Risk Management Governance Survey was conducted between April and May 2021 among 615 respondents across North America, EMEA, APAC and Latin America at organisations with at least 100 employees and $50 million in total annual revenue.
Gartner clients can learn more in “CIOs Need to Rebalance Accountability for Cybersecurity With Business Leaders” and in the complimentary Gartner webinar “Roadmap to Renewal: Insights from the 2022 Board of Directors Survey.”
Fachartikel

Strategien für eine fortgeschrittene digitale Hygiene

Mit LogRhythm 7.16 können Sie das Dashboard-Rauschen reduzieren und Log-Quellen leicht zurückziehen

Wie man RMM-Software mit einer Firewall absichert

Red Sifts vierteljährliche Produktveröffentlichung vom Frühjahr 2024
Konvergiert vs. Einheitlich: Was ist der Unterschied?
Studien

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen

Zunahme von „Evasive Malware“ verstärkt Bedrohungswelle

Neuer Report bestätigt: Die Zukunft KI-gestützter Content Creation ist längst Gegenwart

Neue Erkenntnisse: Trend-Report zu Bankbetrug und Finanzdelikten in Europa veröffentlicht

Studie: Rasantes API-Wachstum schafft Cybersicherheitsrisiken für Unternehmen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
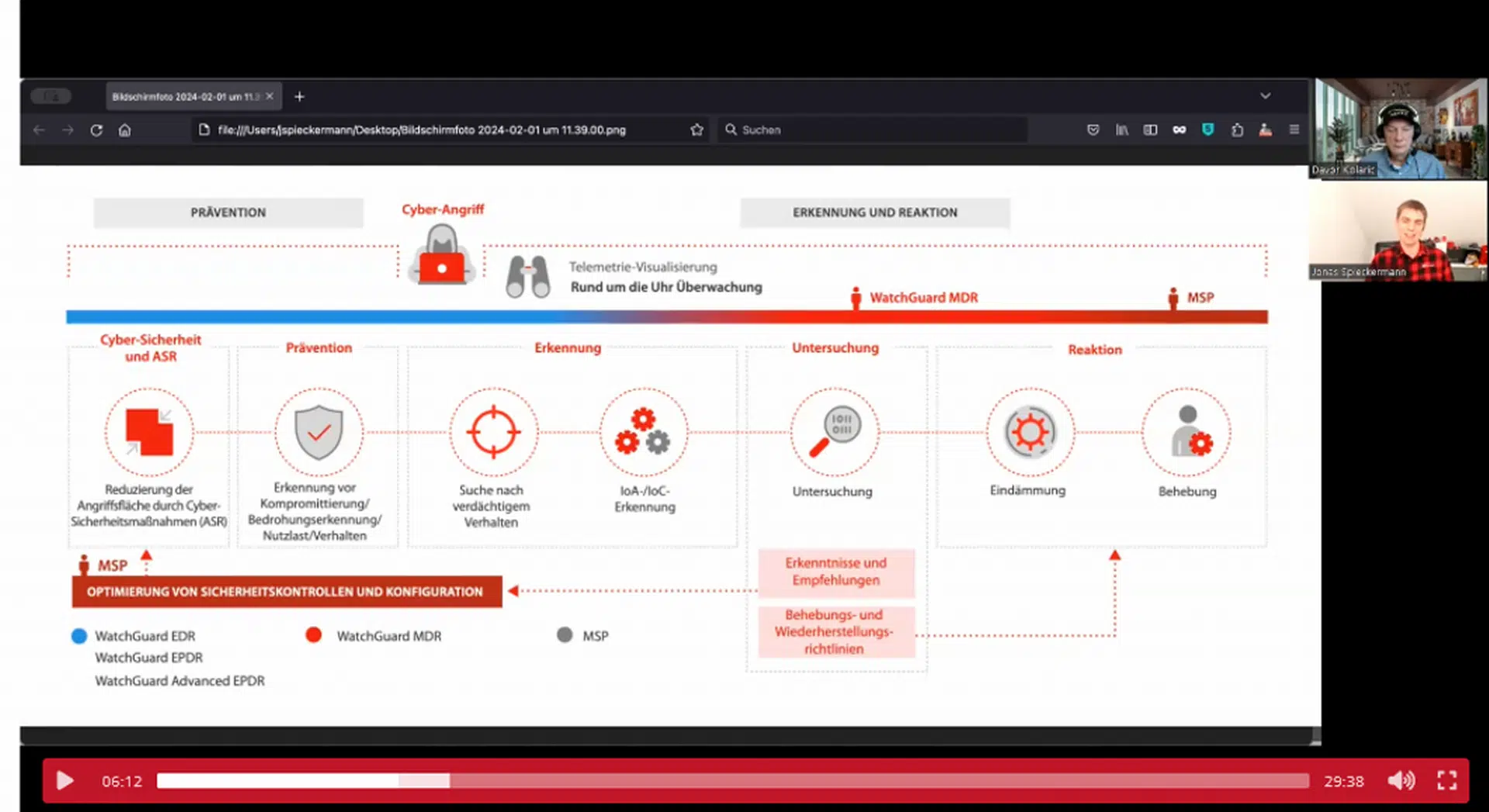
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand