ETSI has recently released ETSI GR SAI 005, a report which summarizes and analyses existing and potential mitigation against threats for AI-based systems. Setting a baseline for a common understanding of relevant AI cyber security threats and mitigations will be key for widespread deployment and acceptance of AI systems and applications. This report sheds light on the available methods for securing AI-based systems by mitigating known or potential security threats identified in the recent ENISA threat landscape publication and ETSI GR SAI 004 Problem Statement Report. It also addresses security capabilities, challenges, and limitations when adopting mitigation for AI-based systems in certain potential use cases.
Artificial intelligence has been driven by the rapid progress of deep learning and its wide applications, such as image classification, object detection, speech recognition and language translation. Therefore, ETSI GR SAI 005 focuses on deep learning and explores the existing mitigating countermeasure attacks.
ETSI GR SAI 005 describes the workflow of machine learning models where the model life cycle includes both development and deployment stages. Based on this workflow, the report summarizes existing and potential mitigation approaches against training attacks (i.e. mitigations to protect the machine learning model from poisoning and backdoor attacks) and against inference attacks, including those from evasion, model stealing, and data extraction. Mitigation approaches are firstly summarized as model enhancement and model-agnostic, and then grouped by their rationales.
Due to the rapid evolvement of attack technology for AI-based systems, existing mitigations can become less effective over time, although their approaches and their rationales remain in place. In addition, most of the approaches presented stem from an academic context and make certain assumptions, which need to be considered when these approaches are applied in practice. ETSI GR SAI 005 intends to serve as a securing AI technical reference for the planning, design, development, deployment, operation, and maintenance of AI-based systems. In future, more research work needs to be done in the area of automatic verification and validation, explainability and transparency, and novel security techniques to counter emerging AI threats.
Download the report CLICKING ON THIS LINK.
Fachartikel
Studien

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen

Zunahme von „Evasive Malware“ verstärkt Bedrohungswelle

Neuer Report bestätigt: Die Zukunft KI-gestützter Content Creation ist längst Gegenwart
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
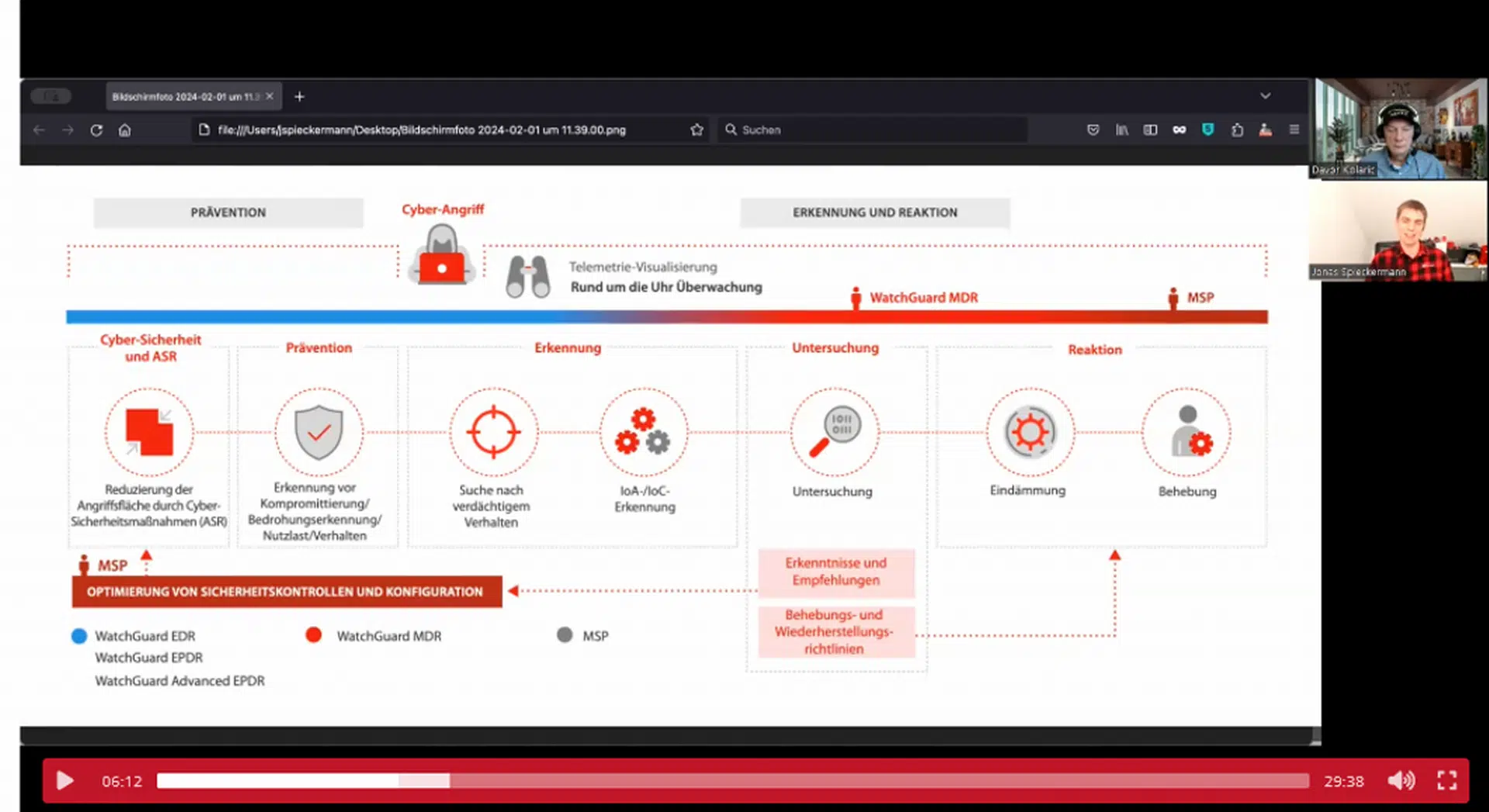
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand