The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity releases two reports on cryptography: one on the progress of post-quantum cryptography standardisation, and the other on exploring the technologies under the hood of crypto-assets.
Cryptography is a vital part of cybersecurity. Security properties like confidentiality, integrity, authentication, non-repudiation rely on strong cryptographic mechanisms, especially in an always connected, always online world.
In addition, cryptography’s applications open up new opportunities and markets: digital signatures or online transactions would not be possible without it. Given its importance, cryptography (encryption) remains a heavily researched field, and even finds its way into the headlines, referred to in high level documents and even legislation.
One such document is the new EU Cybersecurity Strategy (December 2020), which mentions out quantum computing and encryption as key technologies for achieving resilience, technological sovereignty and leadership.
With the objective to support the implementation of the Cybersecurity Strategy and of relevant legislative efforts, ENISA publishes two reports on the topic of cryptography. The first one focuses on the forthcoming disruptions of post-quantum computing on our present cybersecurity infrastructure and how we need to mitigate it. The second one introduces the cryptographic building blocks used in a majority of digital currencies & crypto-assets, which will fall under the scope of a new EU regulatory proposal.
Post Quantum security and why it matters
Quantum technology will enable a huge leap forward in many branches of industry, as it can efficiently resolve problems technologies of today are not able to provide a solution for. However, this technology will be highly disruptive for our current security equipment and systems.
As a matter of fact, scientists commonly agree that quantum computers will be able to break widely used public-key cryptographic schemes. These are the same schemes working behind the green lock in our browser tabs telling us that our data are protected against malicious eavesdroppers. Similarly, these are also the same schemes allowing us to have digital signatures and designed to implement the Electronic identification (eID) and Trust Services of the eIDAs regulation. Consequently, data or processes protected by those schemes, such as bank transactions, software updates, digitally signed official documents, patient records and more, will instantly cease to be secure.
This initiative is motivated by the fact that the transition to new quantum resistant cryptographic algorithms will take years, since the related processes are both extremely intricate and financially costly.
The study – Post-Quantum Cryptography: Current state and quantum mitigation – provides a concise overview of the current progress of the standardisation process of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) schemes. It introduces a framework to analyse existing quantum-safe solutions, classifying them into families and discussing their advantages and shortcomings.
With contributions from top experts in the field, it helps readers navigate an overly complex but also fascinating topic for the future of cybersecurity. The study aims to help decision makers and system designers take up appropriate actions, as soon as possible. To that end, it includes useful quantum resistant techniques that can be implemented in today’s systems until PQC algorithms become standardised and generally available.
Under the hood of crypto assets & the Distributed Ledger Technology
With the creation of a pan-European blockchain regulatory sandbox, the European Union intends to put Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) to the test. Such technologies, also referred to as blockchain technologies, are those on which digital assets such as cryptocurrencies are built upon. But the applications do not stop there, smart contracts, anti-counterfeit seals, even games, have been based on a few important cryptographic building blocks.
The ENISA report – Crypto Assets: Introduction to Digital Currencies and Distributed Ledger Technologies – aims to further increase understanding around these underlying cryptographic components that compose the blockchain and in extension crypto-assets, digital currencies and the host of applications possible.
As a continuation of an earlier report on the security and challenges of DLTs, this report provides an in-depth explanation of the technical components involved and illustrates their uses into popular deployed instances.
By focusing on crypto-assets, ENISA intends to support policymakers by explaining the underling cryptographic mechanics used and raise awareness on foreseen security, financial, legal and data protection issues.
Background
This work falls under the provisions of Articles 5, 8, 9 and 11 of the Cybersecurity Act. ENISA’s Work Programme foresees activities to support Knowledge Building in Cryptographic algorithms.
In cooperation with the European Commission, Member States and other EU bodies, the Agency engages with expert groups to address emerging challenges and promote good practices.
One of these emerging risks arise in relation to quantum computing cryptanalytics capabilities, where there is need to transition to quantum safe encryption as a counter measure and to support EU in advancing its strategic digital autonomy. In addition, the continuation of past ENISA work on blockchain security with a new study looking at the cryptographic components was very timely as it coincided with the EU efforts in regulating crypto-assets and the announcement of the ECB that it is exploring the plausibility of a centrally backed digital euro, to complement the euro banknote.
Further information
ENISA report – Post-Quantum Cryptography: Current state and quantum mitigation
ENISA report – Crypto Assets: Introduction to Digital Currencies and Distributed Ledger Technologies
On the security of personal data: Cryptographic Protocols and Tools
Fachartikel
Studien

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen

Zunahme von „Evasive Malware“ verstärkt Bedrohungswelle

Neuer Report bestätigt: Die Zukunft KI-gestützter Content Creation ist längst Gegenwart
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
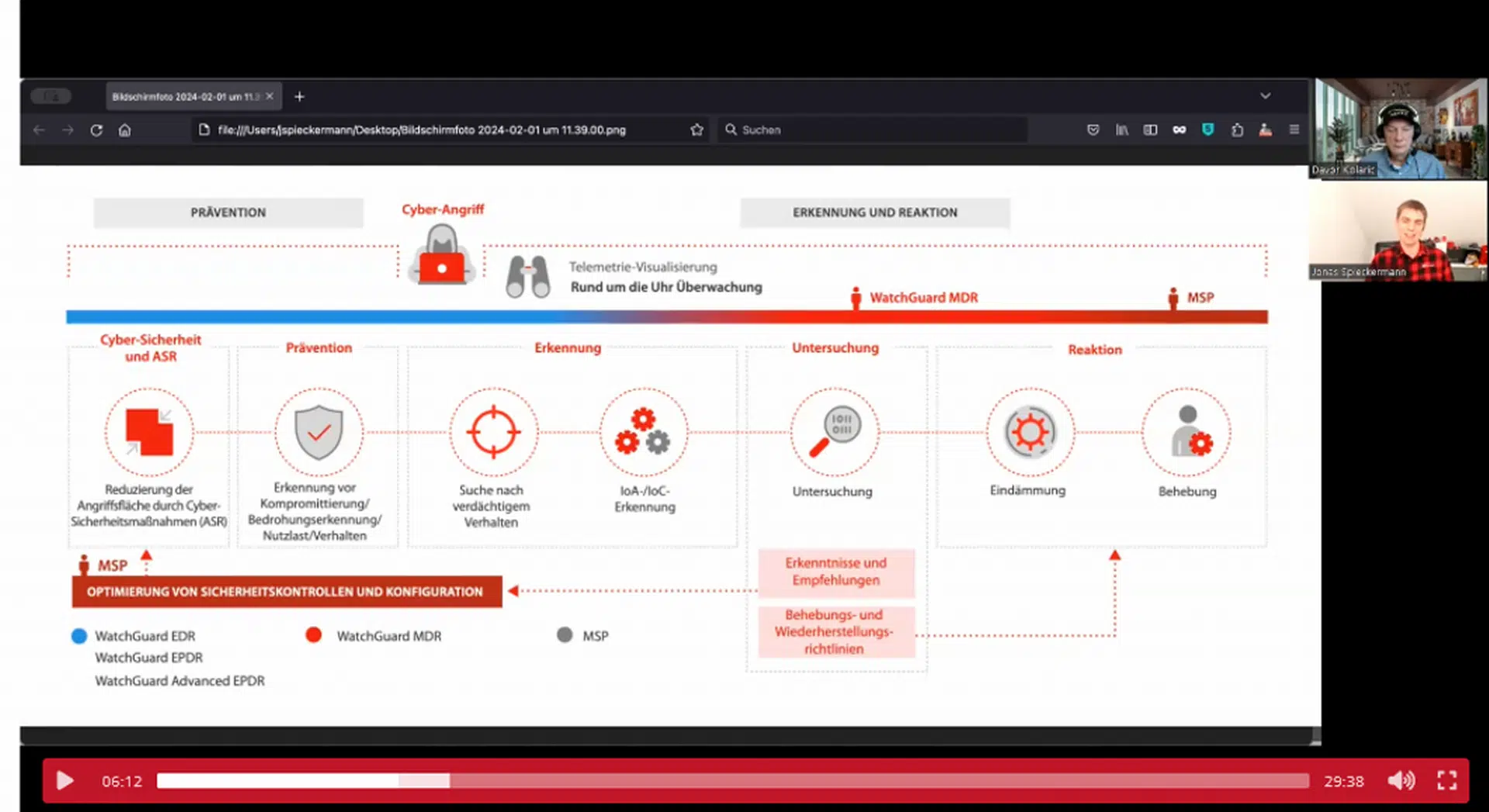
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand