While the semiconductor supply chain is essential to our way of life, its safety is far from guaranteed. Nearly 60% of the global semiconductor industry is based in Taiwan, presenting a potential global crisis if tensions between Taiwan and China continue to grow, according to a new analysis from Interos.
Given Russia’s war in Ukraine, there is concern that China may act on similar territorial ambitions, raising the risk of geopolitical unrest that could further derail the global economy.
The semiconductor industry already finds itself facing numerous challenges in production, including:
- The ongoing trade war between the US and China has raised the cost of certain goods while also limiting access to certain products by blacklisted Chinese companies, demanding compliance teams have real-time insight into the semiconductor supply chain.
- Taiwan and neighboring Japan both face regular disruptions from earthquakes.
- Even before the pandemic, the industry was inundated with clean room contamination events, compromised materials making their way into the process, water supply shortages, cyber-attacks, facility fires, and power outages.
While the United States government has made efforts to develop the semiconductor supply chain within its borders, a shortage of skilled workers has posed a significant threat. According to a recent study, 82% of semiconductor industry executives reported a lack of qualified job candidates.
The challenges in Taiwan and the difficulty of increasing production at home caused shortages for American companies, and there does not appear to be an end in sight. Opinions on the end of the chip shortage range from the second half of 2023 until well into 2024 and beyond.
Read more in the Interos report, which you can download here. Then learn more about how the Interos platform can help navigate the semiconductor supply chain by visiting interos.ai.
Download here.
Fachartikel
Studien

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen

Zunahme von „Evasive Malware“ verstärkt Bedrohungswelle

Neuer Report bestätigt: Die Zukunft KI-gestützter Content Creation ist längst Gegenwart
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
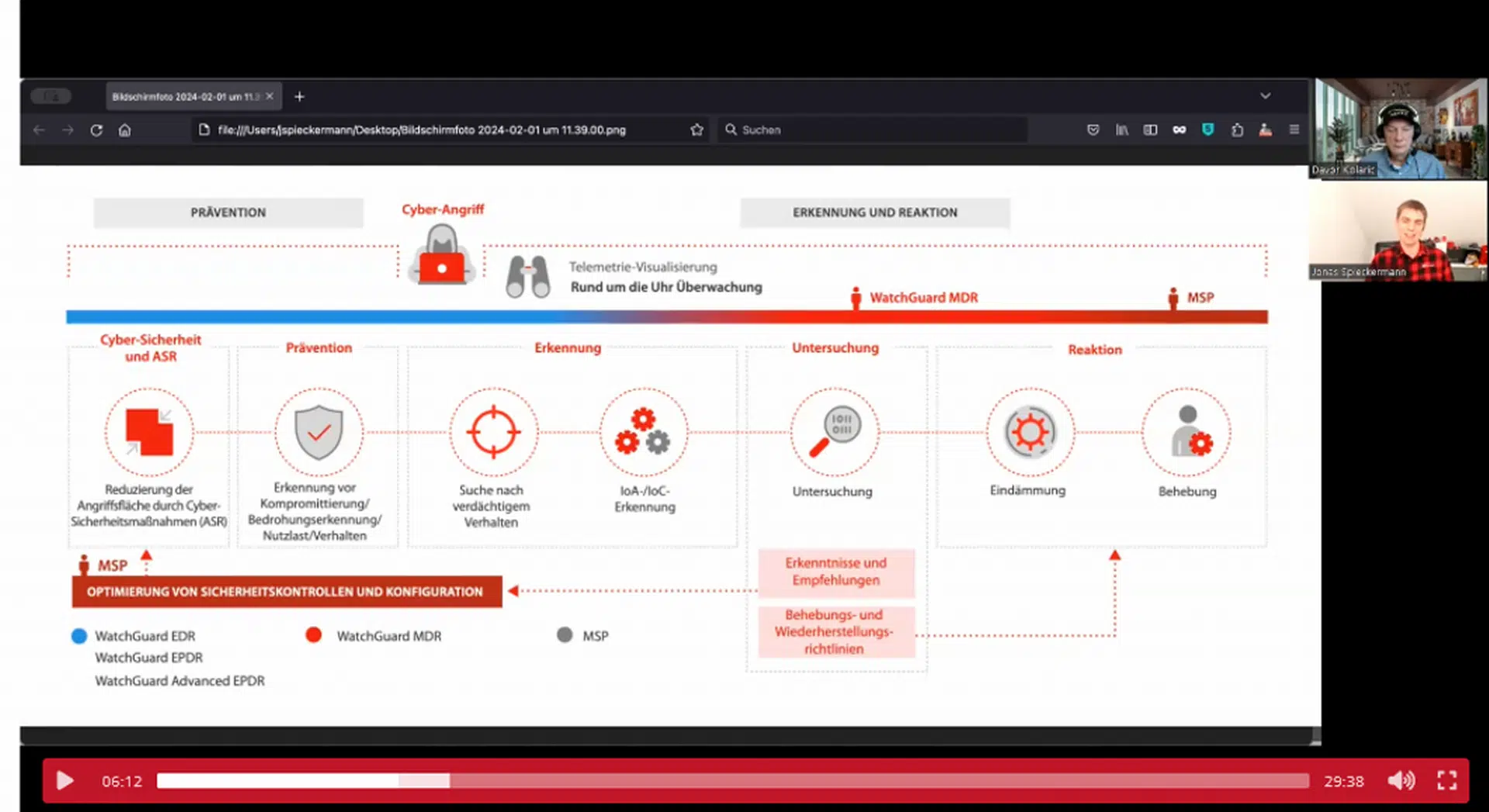
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand