AWS is one of the world’s leading cloud computing platforms. With 34% of the worldwide market share, it offers a comprehensive range of cloud-based services and solutions, including a wide variety of cloud storage tiers.
One of the primary advantages of AWS is its flexibility, which allows businesses to easily adapt their model as they scale up or down. However, as “cloudflation” continues, companies may find that their cloud costs have quickly become unmanageable — or that they’re locked into a more expensive service because of legacy applications.
To keep 2023 budgets under control with rising cloud costs, it’s crucial to understand how to effectively manage costs in AWS.
Understanding AWS offerings
The Amazon AWS cloud computing platform offers a wide range of services and solutions for businesses and developers. The services offered by AWS include compute, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, security, mobile, and developer tools. Since these services are scalable and easily integrated with other applications, AWS has become an extremely popular choice for organizations of all sizes — more popular even than Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, and other major competitors.
Some of the top AWS services include Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), RDS (Relational Database Service), Aurora (a relational database engine), and Lambda (a compute service). Amazon also offers several popular cloud storage tiers:
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS): High-performance block storage service designed for transaction-intensive workloads at any scale.
- Amazon Elastic File System (EFS): Highly elastic and scalable file system that allows users to share file data without provisioning or managing storage.
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3): Highly affordable object storage. S3 is cost-efficient, and scalable, providing significant cost savings compared to other AWS storage types as well as traditional storage like SSDs, NAS and SAN.
- Amazon S3 Glacier and Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive: Archive storage for long-term, infrequently accessed data.
These types of AWS storage meet different operational needs, but they also present drastically different costs. For example, the price of storing 250 TB per year is $921,600 in EFS but only $38,400 in S3 Infrequent Access — a factor of 24.
Below, we’ll explore some of the key strategies that businesses can use to minimize their AWS costs and maximize their cloud investments.
Right-size resources
One of the most significant causes of high AWS costs is over-provisioning of resources. When businesses first start using AWS, they often allocate more resources than they actually need to ensure that their applications have enough capacity. Over time, companies may continue to pay for these resources without ever using them.
This may seem unlikely, but studies show that a surprisingly high number of businesses don’t know where all their data is. One 2022 report revealed that 43% of companies could not identify where their own critical data is located.
To minimize costs in AWS, companies should try right-sizing their resources: only paying for what they need to support their operations. Once organizations have a sense of what data they’re using and where, they can use the AWS Cost Explorer to monitor resource usage from the past 12 months, predict usage for the upcoming 12 months, and identify underutilized services.
Autoscale and automate
Auto-scaling is another effective way to minimize costs in AWS. Auto-scaling allows you to automatically adjust your number of instances based on demand, so that you only pay for the resources that you need. This can help reduce costs, as you won’t be paying for unused resources anymore.
Companies can also automate some aspects of workload optimization in AWS. Instead of manually assessing your current resource usage and allocation, you can use AWS tools like EC2 Auto Scaling, which automatically adjusts the number of Amazon EC2 instances in response to changing demand, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk, which provides a platform for deploying, managing and scaling web applications. These tools reduce the amount of manual intervention required to manage workloads and ensure that resources are being utilized efficiently.
Consider using reserved and spot instances
Reserved and spot instances are both a cost-effective way for some businesses to allocate resources in AWS.
Reserved instances commit a company to using a specific instance type for a specified period of time in exchange for a lower hourly rate. Like other reservation-based offerings, they can be much cheaper than on-demand instances, which are billed at a higher hourly rate. While reserved instances aren’t the right choice for everything, they may be a good fit for applications that have a steady and predictable resource usage pattern.
Spot instances are another cost-saving option in AWS. Spot instances allow organizations to bid on unused Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) capacity, which can be much cheaper than on-demand instances.
Spot instances aren’t right for every team, since they do require setting an appropriate bid price, monitoring availability, and adjusting bids as needed. But they’re ideal for applications that are flexible and for tasks like batch processing and big data analysis that can be interrupted without consequence — and they can help companies cut costs.
Watch out for misconfigurations
Not just a problem for your security team, a misconfiguration in AWS can very much impact your bottom line. For instance, misconfigured buckets can cause downtime, leave your data vulnerable to attack, and even result in expensive data loss.
Breaches caused by misconfigurations can also bring serious fines from failing to meet cross-border data regulations. Likewise, periods of downtime can violate service-level agreements and lead to massive expenses for companies. And that’s not to mention the additional expenses of higher cyber insurance premiums, ransomware payments, and disaster response and recovery that can all stem from accidental data exposure.
Long story short? Avoiding misconfigurations isn’t just a crucial part of good data security; it’s also an important way to prevent major costs for your company.
Don’t let legacy applications slow you down
Many companies want to use durable, cost-effective object storage like S3, but their legacy applications still rely on hard drives, EFS, or EBS. That means that entire applications need to be rewritten to support object storage — a time-consuming and resource-intensive process.
To solve the problem, ShardSecure is helping organizations to optimize their cloud usage and protect their data in AWS, including in multi- and hybrid-cloud infrastructures — without ever rewriting applications, redesigning data flows, or changing their user experience.
With ShardSecure’s transparent plug-and-play technology, companies can easily leverage object storage like AWS S3 and enjoy vastly improved data security and resilience. ShardSecure’s performance is also very similar to EFS’s, so data access remains fast and easy for users.
To learn more about the ShardSecure solution and cost savings in AWS, take a look at our white paper.
Conclusion
The cloud can be an invaluable tool that helps companies excel, or it can be a budgetary black hole. As one of the world’s top cloud service providers, AWS offers myriad solutions for companies to take advantage of — but only if they know how to maximize their cloud investments. With the right approach, AWS can be a cost-effective solution for your organization’s computing needs and a priceless tool on the path to future success.
For more information about data privacy, security, and resilience in the cloud, visit ShardSecure’s resources page.
Sources
Chart: Amazon, Microsoft & Google Dominate Cloud Market | Statista
Why Your Cloud Expenses Are Rising: Blame Cloud-flation | Transforming Data with Intelligence
More Than 40% of Companies Don’t Know Where Their Data Is Stored | Lepide
AWS Cost Explorer | Amazon Web Services
Managing Your Cost Savings with Amazon Reserved Instances | AWS Cloud Enterprise Strategy Blog
Fachartikel

Strategien für eine fortgeschrittene digitale Hygiene

Mit LogRhythm 7.16 können Sie das Dashboard-Rauschen reduzieren und Log-Quellen leicht zurückziehen

Wie man RMM-Software mit einer Firewall absichert

Red Sifts vierteljährliche Produktveröffentlichung vom Frühjahr 2024
Konvergiert vs. Einheitlich: Was ist der Unterschied?
Studien

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen

Zunahme von „Evasive Malware“ verstärkt Bedrohungswelle

Neuer Report bestätigt: Die Zukunft KI-gestützter Content Creation ist längst Gegenwart

Neue Erkenntnisse: Trend-Report zu Bankbetrug und Finanzdelikten in Europa veröffentlicht

Studie: Rasantes API-Wachstum schafft Cybersicherheitsrisiken für Unternehmen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
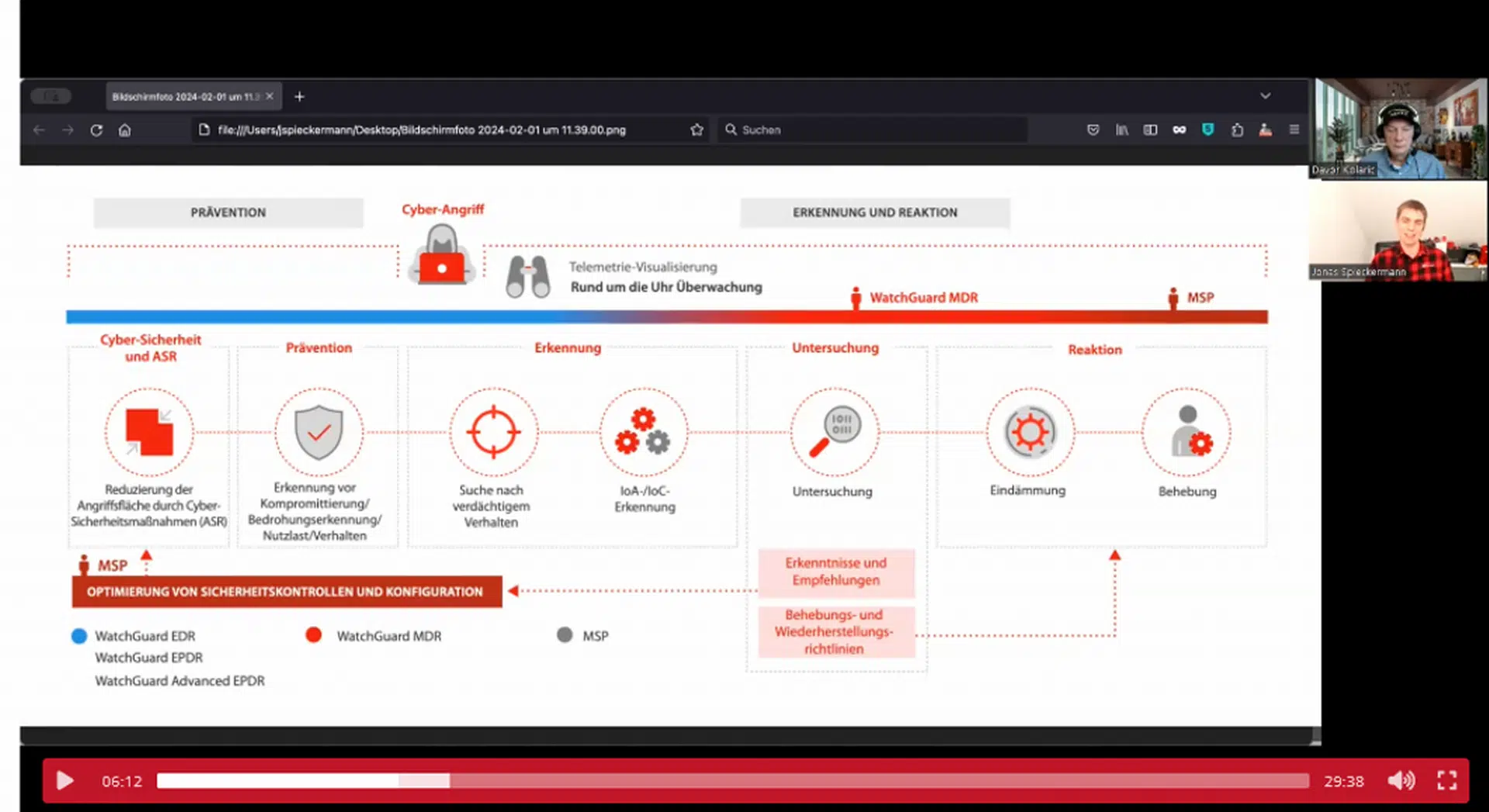
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand