Understanding data is one of the first and most important steps to protecting it. Without knowing what kinds of data you’re processing and storing, it’s impossible to ensure strong privacy and security.
Understanding data isn’t a small task, either: It’s estimated that 97 zettabytes of data were created worldwide in 2022. To put it into perspective, that’s enough data to store 48.5 trillion full-length movies.
Today, we’ll break down the most common data type, unstructured data, to help you understand everything you need to know. We’ll also explore ShardSecure’s solution for unstructured data protection in on-prem and cloud environments.
The three types of data
The vast majority of data falls into one of three categories: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Here’s the breakdown:
Structured data. As its name suggests, structured data has been organized. Structured data resides in a relational database and can be mapped into certain fields to analyze and manage information more simply.
Semi-structured data. Less commonly discussed, semi-structured data does not reside in a database but still has some organizational properties for easier analysis.
Unstructured data. Finally, unstructured data is simply data that is not or cannot be organized into a typical relational database. This includes a wide range of both human- and machine-generated materials, as we’ll discuss below.
What’s so special about unstructured data?
It’s everywhere.
First, unstructured data is omnipresent in the modern workplace. It includes everything from Word docs and weather data to smartphone sensor reports. Here are just a handful of examples of unstructured data:
- PDFs
- Images
- Social media content
- Journal and magazine articles
- Songs and audio files
- Financial documents
- Medical records
- Full-length motion pictures
- Surveillance data
- IoT sensor reports
- Machine learning datasets
As you can imagine, the sheer amount and variety of unstructured data can pose major organizational and security challenges. Unstructured datasets at the enterprise level can contain tens of billions of items, ranging from just a few bytes to many terabytes in size.
It already makes up the majority of data, and it’s growing fast
Estimates show that 80-90% of data is unstructured data. That presents major challenges, since unstructured data doesn’t adhere to conventional data models — but it also presents major opportunities. MIT Sloan describes unstructured data as a “huge untapped resource with the potential to create competitive advantage for companies that figure out how to use it.”
Unstructured data is also growing rapidly. It’s expected to rise from 33 zettabytes in 2018 to 175 zettabytes — that’s 175 followed by 21 zeroes — by 2025.
Even so, companies still tend to underestimate their data growth, as the data management provider Komprise’s president and COO Krishna Subramanian explained.
“For every piece of data, companies typically keep a few backup copies and a replication copy for disaster recovery,” she said. “If you think your data is growing at 30%, it’s more like 90-100% when you factor in all the copies of the data.”
It’s a vital part of machine learning.
Unstructured data is one of the most important drivers of machine learning. As the AI Infrastructure Alliance notes, unstructured datasets have powered autonomous boats across the Atlantic and through the canals of Amsterdam. They’ve helped Teslas drive hands-free and customer service lines recognize your speech when you call in.
While unstructured data is much more complicated for businesses to process than structured data, it’s also extremely useful for building sophisticated predictive models. Although we’re still in the early stages of AI and machine learning, the use of unstructured data in models is going to be increasingly important as these technologies develop.
It’s underprotected.
While structured data can be secured relatively easily by restricting access to databases, unstructured data exists in many file types and across many different devices, programs, and storage systems. This makes it more difficult to track — and more challenging to protect.
Unstructured data is also likely to contain sensitive information, from legal documents and confidential emails to source code, design files, and other IP. To keep all these kinds of sensitive data safe from unauthorized access, companies need a reliable data protection solution.
Protecting your unstructured data with ShardSecure
ShardSecure offers easy, agentless protection for unstructured data in on-prem, cloud, and multi-cloud environments. Our innovative approach to file-level encryption prevents unauthorized data access by everyone from infrastructure providers and cloud administrators to malicious hackers and ransomware gangs. This supports strong data privacy as well as compliance with cross-border data regulations like the GDPR.
Our Data Control Platform integrates seamlessly with existing applications and storage locations, meaning that workflows do not need to be redesigned. Employees can continue accessing, editing, and sharing their unstructured data files exactly as usual while enjoying advanced data protection.
To learn more about our technology, take a look at our resources page.
Sources
85+ Big Data Statistics You Should Know in 2023 | G2
Difference Between Structured, Semi-Structured, and Unstructured Data | GeeksforGeeks
8 Examples of Unstructured Data | Treehouse Tech Group
What Is Unstructured Data? Structured Data vs Unstructured | NetApp
Tapping the Power of Unstructured Data | MIT Sloan
Why Unstructured Data is the Future of Data Management | VentureBeat
Unstructured Data – The Unsung Hero of Machine Learning | AI Infrastructure Alliance
3 Use Cases for Unstructured Data | Transforming Data with Intelligence
Structured vs. Unstructured Data: A Comprehensive Guide | Digital Guardian
Fachartikel
Studien

Drei Viertel aller DACH-Unternehmen haben jetzt CISOs – nur wird diese Rolle oft noch missverstanden

AI-Security-Report 2024 verdeutlicht: Deutsche Unternehmen sind mit Cybersecurity-Markt überfordert

Cloud-Transformation & GRC: Die Wolkendecke wird zur Superzelle

Threat Report: Anstieg der Ransomware-Vorfälle durch ERP-Kompromittierung um 400 %

Studie zu PKI und Post-Quanten-Kryptographie verdeutlicht wachsenden Bedarf an digitalem Vertrauen bei DACH-Organisationen
Whitepaper
Unter4Ohren

Datenklassifizierung: Sicherheit, Konformität und Kontrolle

Die Rolle der KI in der IT-Sicherheit
CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 – Einblicke in die aktuelle Bedrohungslandschaft
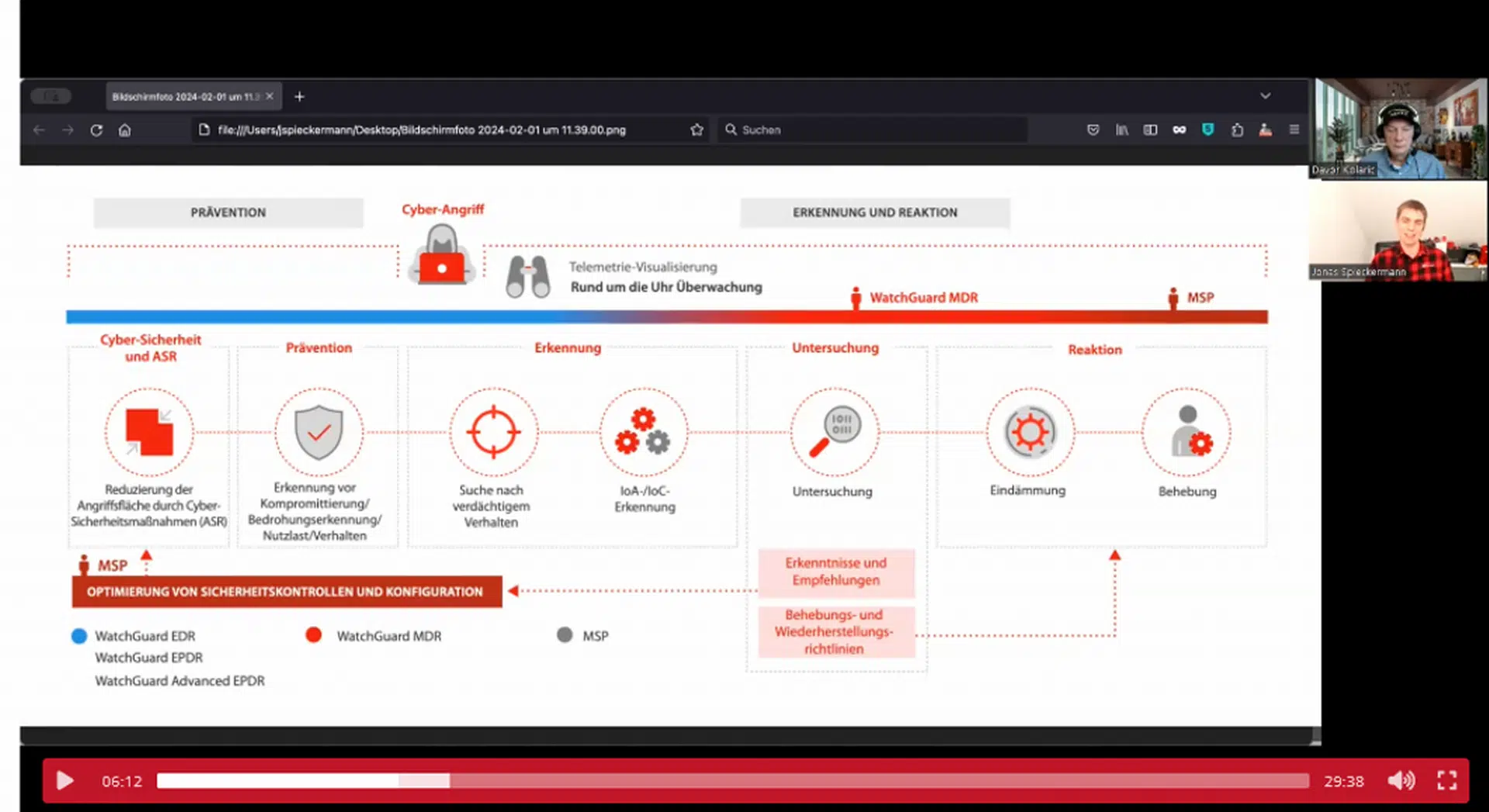
WatchGuard Managed Detection & Response – Erkennung und Reaktion rund um die Uhr ohne Mehraufwand